
Critical Care Education …
On Your Terms.
“Change is inevitable, but transformation is by conscious choice.”
Educational material dedicated to helping you level up your ICU skills.
What It Is:
A library of 24 educational videos with associated lecture slides and adjunct templates/visual aids teaching provider management of the acute patient.
How It Is Different:
Teaching style begins with a brief review of pathophysiology so that you can understand the why before the how. Most lectures include a case study and focus on application.
Presentation style is dynamic and casual - I despise attending lectures where an academic reads words from a power point.
Evidence based with reference links as well as a focus on the most helpful resources to add to your arsenal.
Who It Is For:
Ideal for anyone new to ICU level of care. The content is focused on patho-physiology and management and is intended to train new ICU providers.
Members have included nurses, respiratory therapists, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, EMS providers, even a medical resident.
Now converted to a vault containing instant access to 24 video lectures, PDF slides, templates, visual aids. At this time there are no live lectures.
Recent Lectures…
Templates Created For The Lectures

Learning to write notes is a difficult trajectory.
Watch this quick video to see how mastering your own EMR’s built in technology will serve you well in regards to gaining traction with your growth.
These books are a how-to for H&P note writing. But they are so much more than that. They include a copy/paste ready dotphrase for the most commonly encountered problems in critical care as well as a teaching section for each problem. A “behind-the-scenes” if you will, sharing what I teach NP students about the pathophysiology, forming a differential diagnosis, and developing an evidence-based treatment plan.
The Ultimate H&P Cheatsheet
The newly written 2nd edition includes expanded details.
Truly the most common diagnoses you will see.
Each problem/diagnosis begins with some teaching pages.
A thorough; evidence based plan is presented.
The sample, which applies to the fictitious patient presented is a great copy/paste to use in your EMR. You simply edit to suit your population/protocols.
There is a reference sheet including what I consider to be the MOST helpful resources in learning these diagnoses.
The Ultimate H&P Cheatsheet Companion
Volume 2 is now available!
11 of the next most common diagnoses.
A new patient scenario with a set of associated problems. I do include some bonus diagnoses at the end which are variations of a few diagnoses introduced in the first book.
Same presentation format as the first book: a few pages of teaching followed by a sample.
Months of research combined with my years of experience were poured into this book so that you can fast track your learning.
These dot phrase samples are ready to go for you so all you have to do is load them in your EMR and get busy seeing patients.
Buy both books in physical and electronic formats and save $$$
⭐️ Testimonials ⭐️







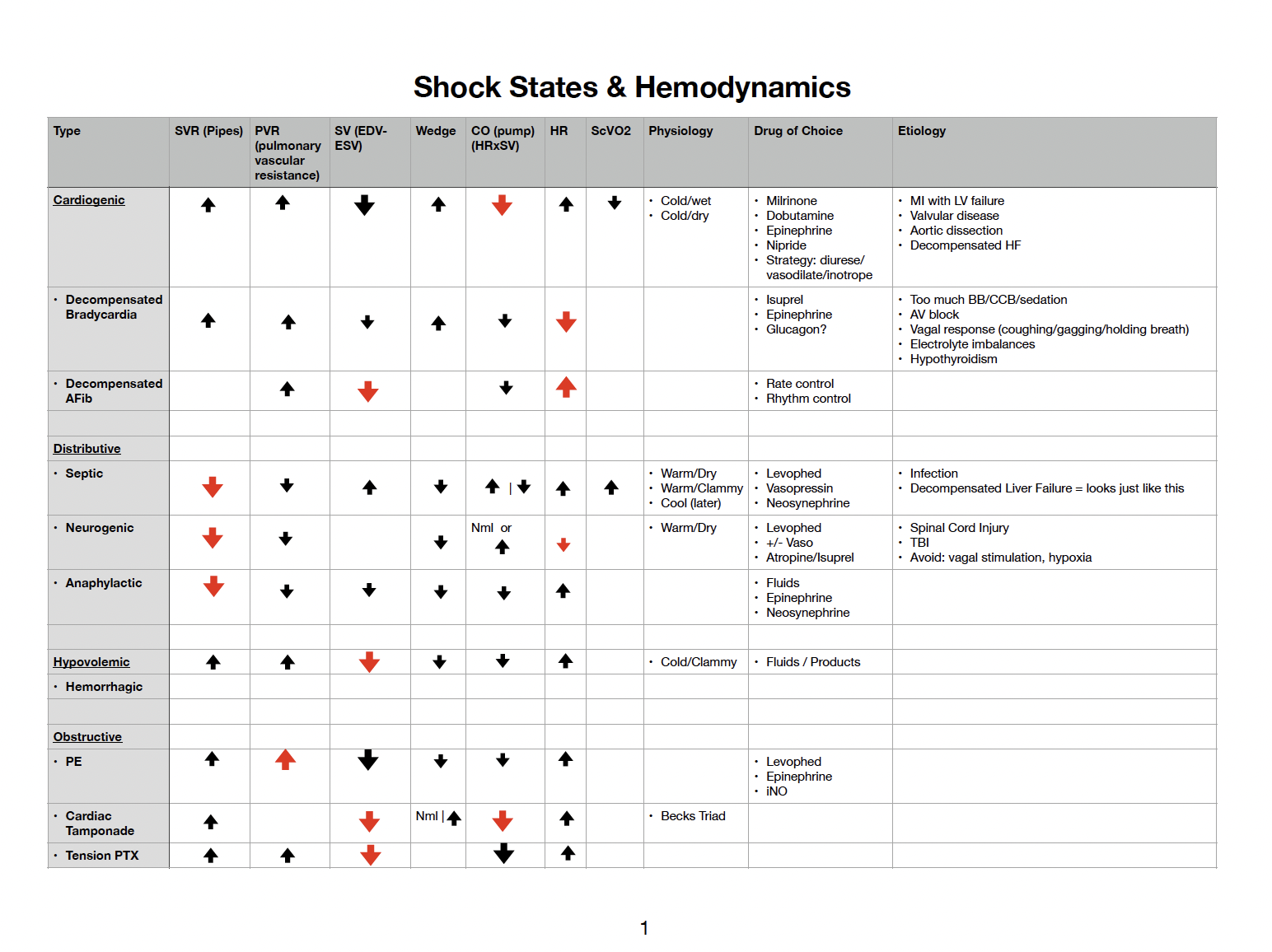
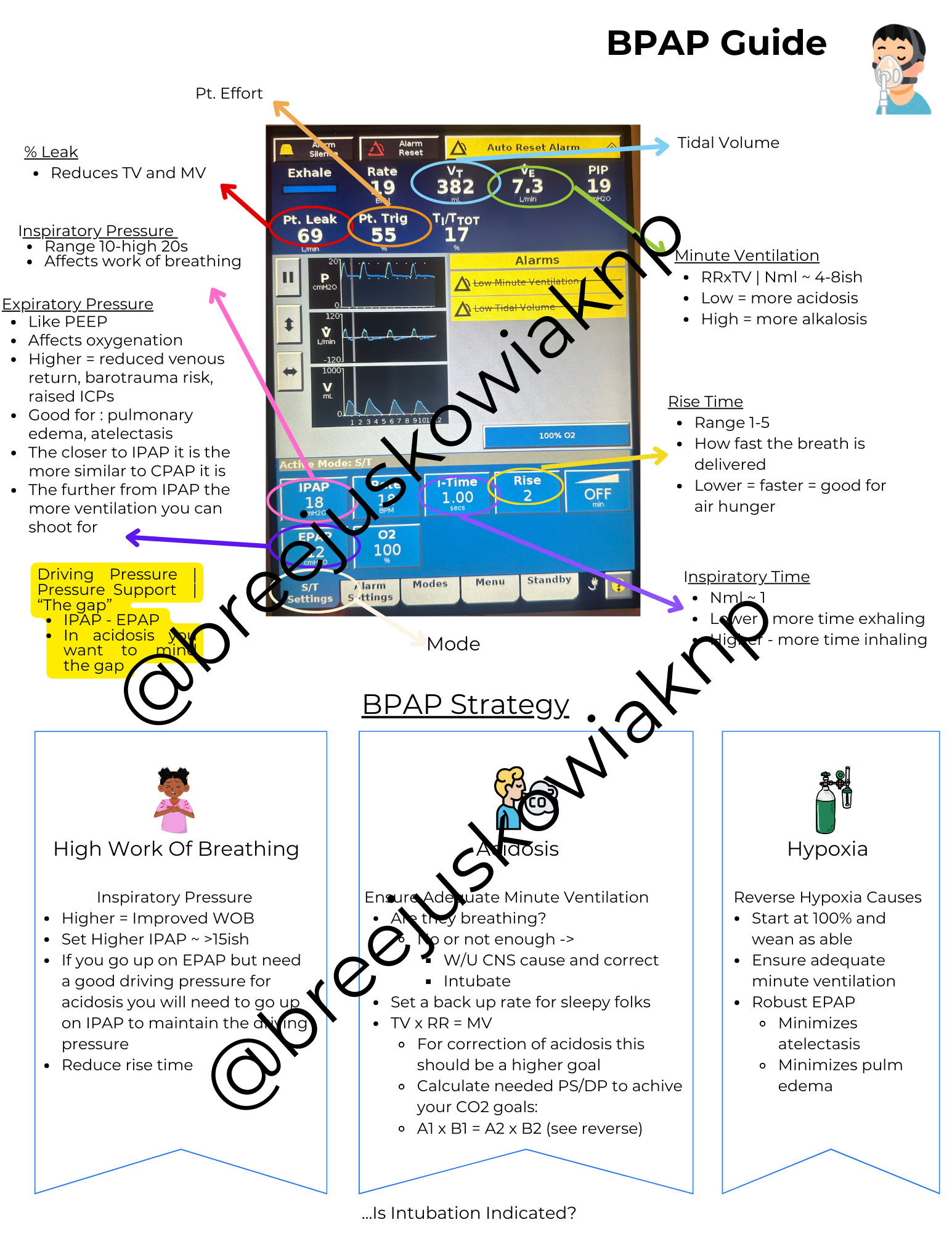


















Case Study
Favorite adjunctive resources
Brief physiology review
S/S of high and low sodium levels and assigning severity
Diagnosing the type of derangement
Narrowing the etiology differentials
When to treat and when to leave them alone
How to treat
Pitfalls to avoid in management
When to consult nephrology